Tuberculosis
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can involve other parts of the body.
How Does Tuberculosis Spread?
- TB bacteria spread through the air when a person with active TB in the lungs coughs, releasing bacteria into the environment. Children exposed to an individual with active TB—particularly within the household—are at risk of contracting the infection.
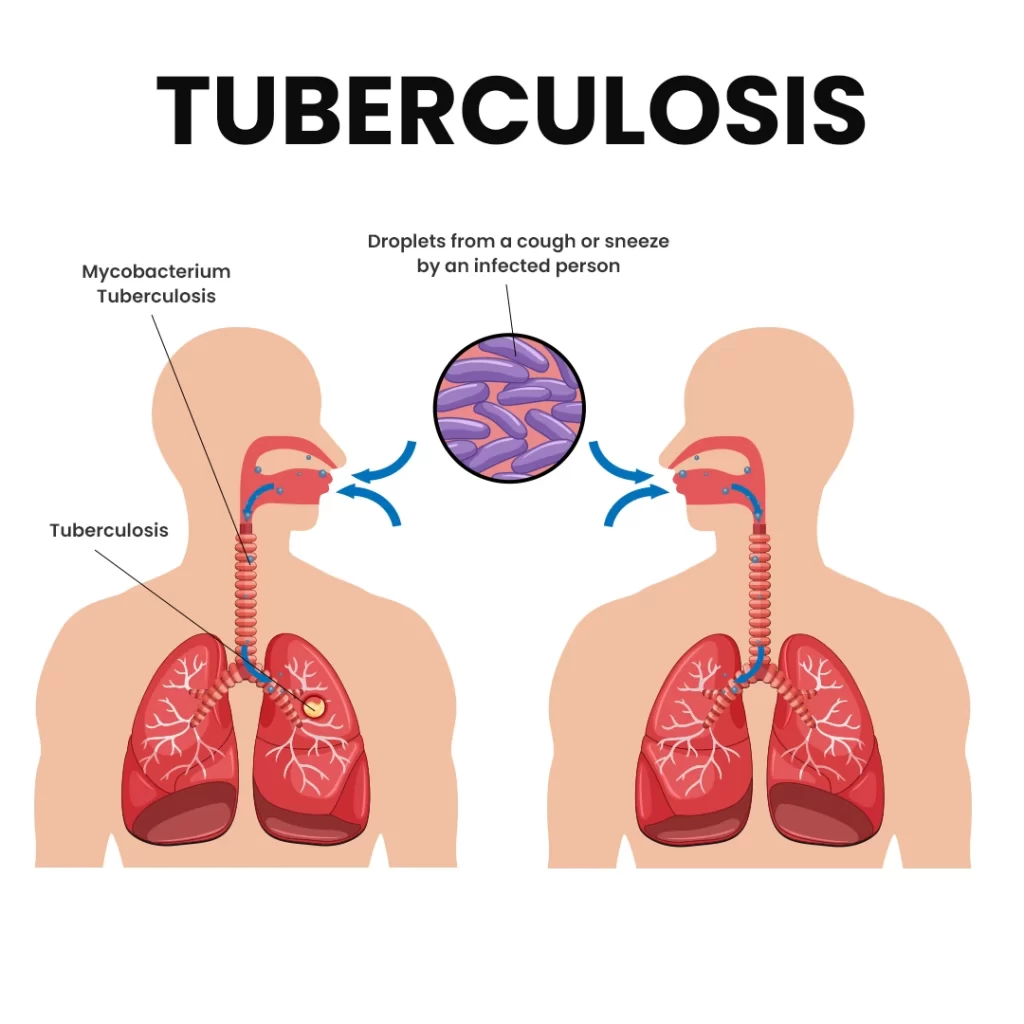
How Common is Tuberculosis in Children in India?
- In 2020, approximately 10 million new TB cases were reported globally, including 1.1 million in children. India accounted for around 33% of total TB cases, with children making up 6-7% of cases in the country.
Which Children Are at Higher Risk for Tuberculosis?
While TB can affect children of any age, some groups are more vulnerable:
- Infants and young children (especially under 1 year), as TB in young children can spread through the bloodstream and cause complications like meningitis.
- Children with close family contact with a person who has active TB.
- Children on immune-suppressing medications, such as steroids or chemotherapy.
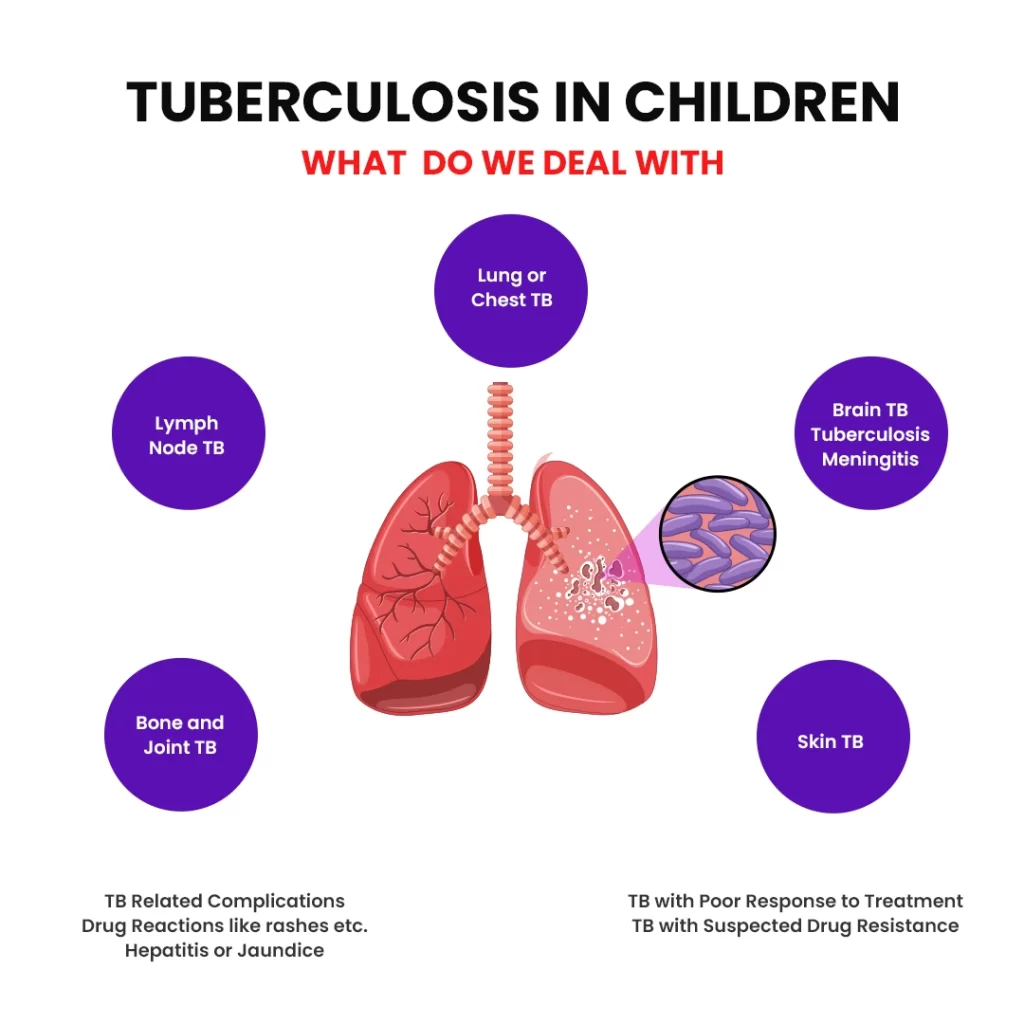
What Parts of the Body Does Tuberculosis Affect?
TB can involve any part of the body. The most commonly affected areas are:
- Lungs
- Lymph nodes
- Abdomen
- Brain
- Other less common areas include the bones and skin.
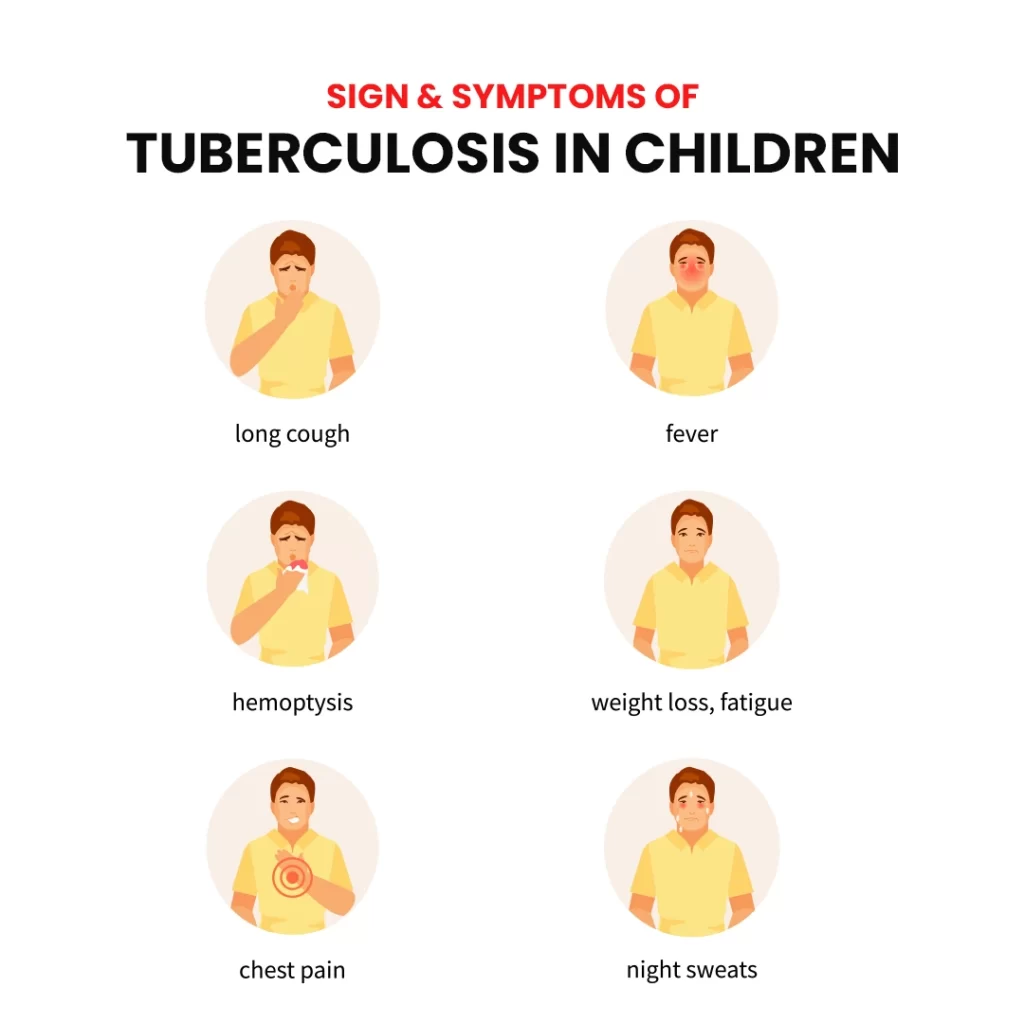
What Are the Symptoms of Pulmonary TB in Children?
Symptoms of pulmonary TB include:
- Persistent cough lasting more than two weeks
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Poor appetite
- General weakness
Is Tuberculosis Curable?
- Yes, TB is curable with anti-tuberculosis medications. Treatment typically lasts 6-9 months depending on the severity and extent of the disease.
