Sleep Disorders
Sleep Disorders
Importance of Sleep for Children:
Sleep is crucial for children, as it is as essential as food, water, and safety. Here are some key roles that sleep plays in their development:
- Tissue Growth and Repair: Sleep facilitates enhanced tissue growth and repair in the body.
- Brain Restoration: Sleep contributes to the restoration of brain tissue, helping with overall cognitive function.
- Energy Conservation: Sleep conserves energy, with metabolic rates dropping to about 10% of daytime levels.
- Learning and Memory: Adequate sleep is vital for learning, retention of new information, and the encoding and consolidation of memories. It also helps eliminate unnecessary information.

Adequate Sleep Duration for Children:
- The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends specific sleep durations based on age, which are important for optimal health and development.

What is Healthy Sleep?
Healthy sleep involves:
- Falling asleep quickly,
- Staying asleep through the night,
- Waking up without difficulty each morning,
- Not feeling drowsy during the day.
What is Sleep Hygiene?
Sleep hygiene refers to a range of practices and habits that contribute to good nighttime sleep quality and alertness during the day.
Tips to Improve Sleep Hygiene in Children:
- Consistent Bedtimes and Waketimes: Establish age-appropriate bedtimes and waketimes to ensure sufficient sleep duration.
- Calming Bedtime Routines: Implement brief calming routines such as baths, massages, or storytelling, especially for infants and preschoolers.
- Sleep-Only Bedrooms: Designate the bedroom for sleeping only; ensure it is dark, cool, and quiet.
- Limit Electronics: Keep electronics out of children’s bedrooms to reduce distractions.
- Encourage Physical Activity: Promote regular physical activity during the day.
- Foster Independent Sleep: Encourage children to fall asleep on their own.
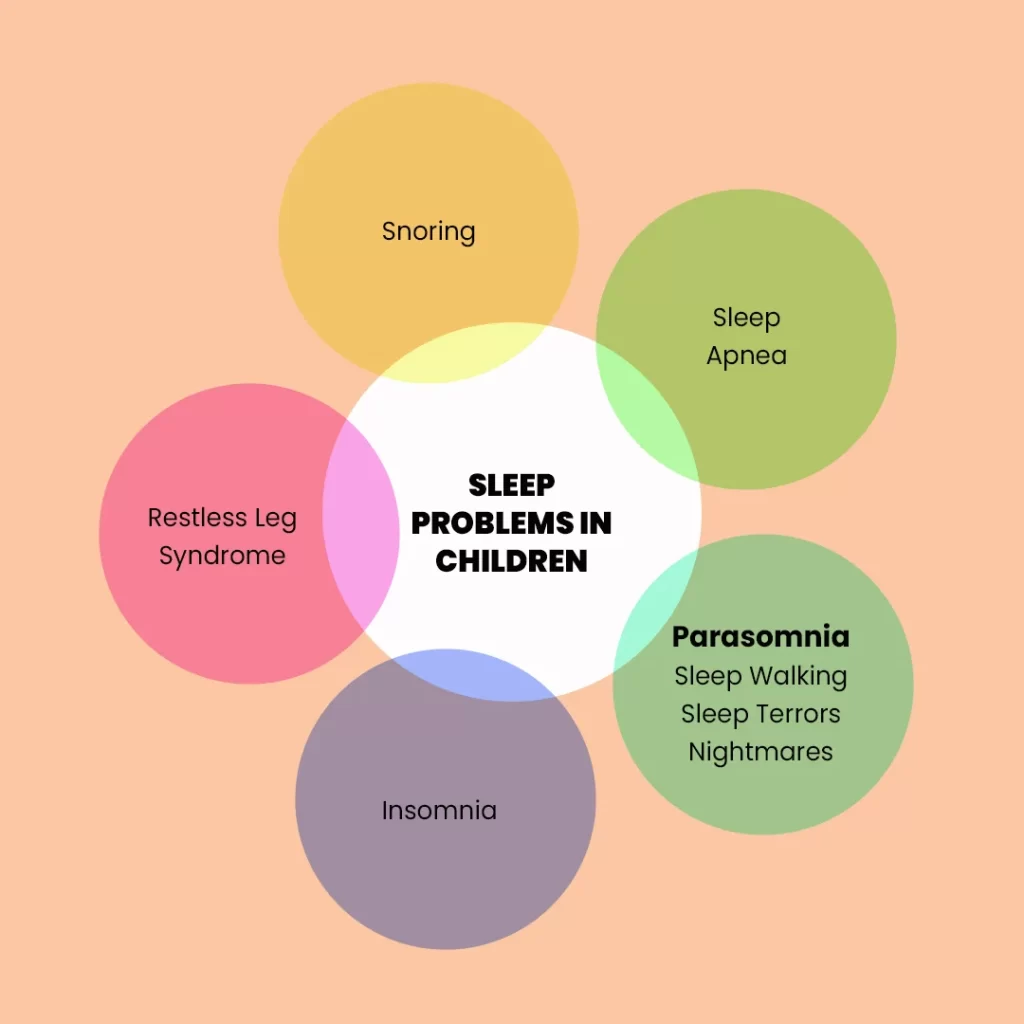
Common Sleep Problems in Children:
Sleep problems in children can manifest in various forms, including:
- Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders (SRBD): The most common type is obstructive sleep apnea, where breathing is interrupted during sleep.
- Parasomnias: Disorders of arousal that include sleepwalking, sleep talking, and night terrors.
- Insomnia: Difficulties with initiating sleep or staying asleep.
- Central Disorders of Hypersomnolence: Disorders associated with excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders: Alterations in the sleep-wake cycle that affect overall sleep patterns.
- Sleep-Related Movement Disorders: Abnormal movements during sleep, such as restless legs syndrome.