Congenital Lung Diseases
Congenital lung malformations refer to abnormalities in the lungs that are present at birth. These conditions arise during the development of the lungs in the womb.
Detection During Pregnancy:
Ultrasound Anomaly Scan:
– Some congenital lung malformations can be detected during routine anomaly scans.
– If a lesion is identified, the mother is usually monitored in collaboration with fetal medicine specialists to assess the situation.
Presentation Later in Life:
- Delayed Symptoms:
– Many congenital lung issues may not present symptoms immediately at birth.
– They can manifest later in life, often with recurrent pneumonia or other respiratory symptoms.
– Some conditions might be discovered incidentally on a chest X-ray performed for unrelated reasons.
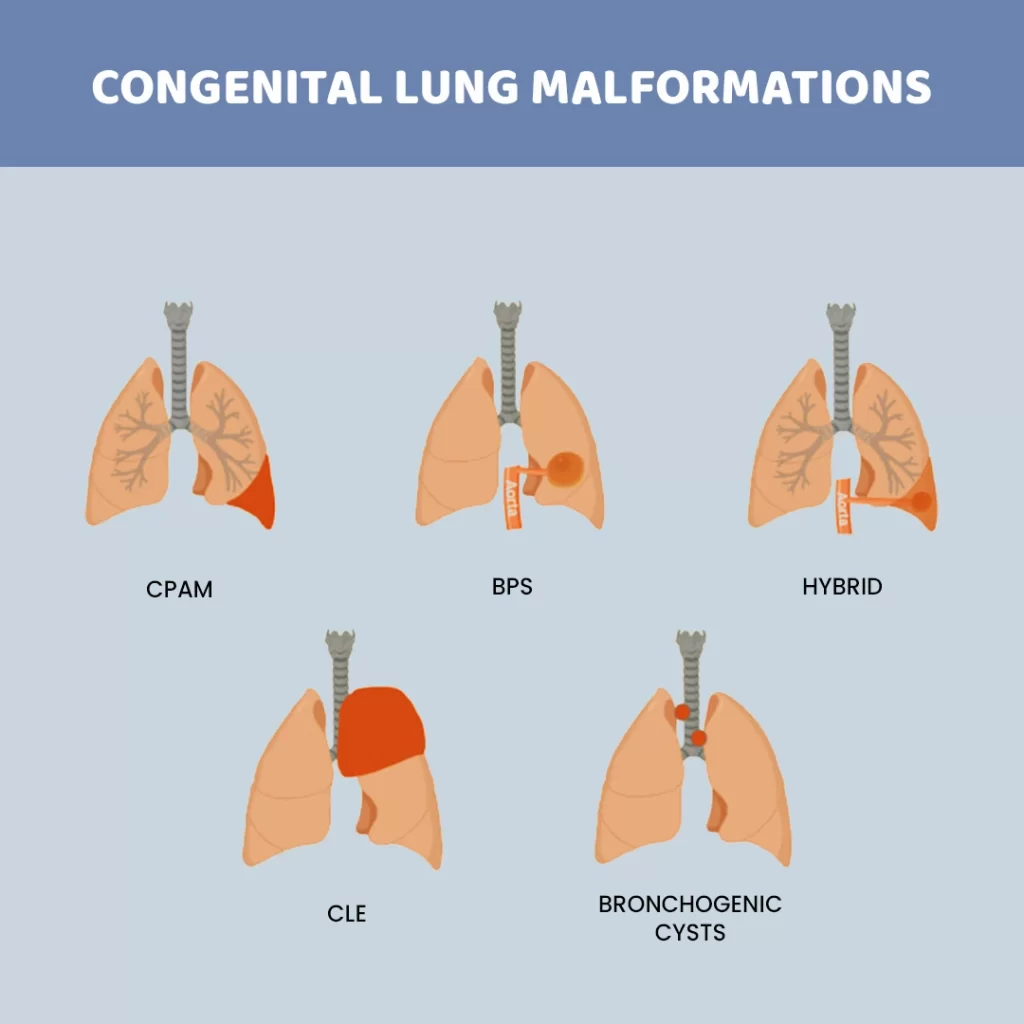
Types of Congenital Lung Lesions:
Congenital lung lesions encompass a wide variety of abnormalities, which can affect the airways, lung parenchyma, or mediastinal structures (the area between the lungs). The most common types include:
Cysts:
These are abnormal, closed sacs within the lungs that can contain fluid.
They can be classified as:
– Cystic: filled primarily with fluid.
– Solid: containing tissue or other solid matter.
– Mixed: containing both cystic and solid components.
Diagnosis:
- Initial Evaluation:
– Suspected congenital lung malformations can often be identified on a chest X-ray. - Confirmatory Imaging:
– A CT scan of the chest is typically required to confirm the diagnosis and provide detailed information about the nature of the malformation.
Treatment Options:
- Individualized Approach:
– Treatment depends on the type, size, and symptoms of the malformation.
– Some malformations may be small and asymptomatic, requiring no immediate intervention, while others could pose significant risks to the child’s health. - Surgical Intervention:
– Many congenital lung malformations that involve lung parenchyma or mediastinal structures may necessitate surgical intervention, especially if they are large or symptomatic.
– The specific surgical approach would depend on the malformation’s characteristics and the child’s overall health.
